做的比较早的海淘网站网站策划是什么
文章目录
- 1. 状态初始化总流程梳理
- 2.创建StreamOperatorStateContext
- 3. StateInitializationContext的接口设计。
- 4. 状态初始化举例:UDF状态初始化
在TaskManager中启动Task线程后,会调用StreamTask.invoke()方法触发当前Task中算子的执行,在invoke()方法中会调用restoreInternal()方法,这中间包括创建和初始化算子中的状态数据。
另外在invoke中,可以通过判断任务状态来判断是否需要初始化状态。
// Allow invoking method 'invoke' without having to call 'restore' before it.if (!isRunning) {LOG.debug("Restoring during invoke will be called.");restoreInternal();}
StreamTask调用initializeStateAndOpenOperators()方法对当前Task中所有算子的状态数据进行初始化。
RegularOperatorChain.
public void initializeStateAndOpenOperators(StreamTaskStateInitializer streamTaskStateInitializer) throws Exception { Iterator var2 = this.getAllOperators(true).iterator(); while(var2.hasNext()) { StreamOperatorWrapper<?, ?> operatorWrapper = (StreamOperatorWrapper)var2.next(); StreamOperator<?> operator = operatorWrapper.getStreamOperator(); operator.initializeState(streamTaskStateInitializer); operator.open(); } }
找到了算子状态初始化的位置,我们继续了解状态是如何初始化的。
1. 状态初始化总流程梳理
AbstractStreamOperator.initializeState中描述了状态初始化的总体流程,如下代码以及注释:
# AbstractStreamOperator.initializeStatepublic final void initializeState(StreamTaskStateInitializer streamTaskStateManager) throws Exception { //1. 获取类型序列化器final TypeSerializer<?> keySerializer = config.getStateKeySerializer(getUserCodeClassloader()); //2. get containingTaskfinal StreamTask<?, ?> containingTask = Preconditions.checkNotNull(getContainingTask()); final CloseableRegistry streamTaskCloseableRegistry = Preconditions.checkNotNull(containingTask.getCancelables()); //3. create StreamOperatorStateContextfinal StreamOperatorStateContext context = streamTaskStateManager.streamOperatorStateContext( getOperatorID(), getClass().getSimpleName(), getProcessingTimeService(), this, keySerializer, streamTaskCloseableRegistry, metrics, config.getManagedMemoryFractionOperatorUseCaseOfSlot( ManagedMemoryUseCase.STATE_BACKEND, runtimeContext.getTaskManagerRuntimeInfo().getConfiguration(), runtimeContext.getUserCodeClassLoader()), isUsingCustomRawKeyedState()); //4. create stateHandlerstateHandler = new StreamOperatorStateHandler( context, getExecutionConfig(), streamTaskCloseableRegistry); timeServiceManager = context.internalTimerServiceManager(); //5. initialize OperatorStatestateHandler.initializeOperatorState(this); //6. set KeyedStateStore in runtimeContextruntimeContext.setKeyedStateStore(stateHandler.getKeyedStateStore().orElse(null));
}
在StreamOperator初始化状态数据的过程中,首先从StreamTask中获取创建状态需要的组件,例如托管状态的管理后端KeyedStateBackend、OperatorStateBackend以及原生状态管理的KeyedStateInputs和OperatorStateInputs组件。
状态数据操作过程中使用的管理组件最终都会封装成StateInitializationContext并传递给子类使用,例如在AbstractUdfStreamOperator中,就会使用StateInitializationContext中的信息初始化用户定义的UDF中的状态数据。
2.创建StreamOperatorStateContext
接下来看如何在Task实例初始化时创建这些组件,并将其存储在StreamOperatorStateContext中供算子使用,如下代码:
StreamTaskStateInitializerImpl
@Override
public StreamOperatorStateContext streamOperatorStateContext( @Nonnull OperatorID operatorID, @Nonnull String operatorClassName, @Nonnull ProcessingTimeService processingTimeService, @Nonnull KeyContext keyContext, @Nullable TypeSerializer<?> keySerializer, @Nonnull CloseableRegistry streamTaskCloseableRegistry, @Nonnull MetricGroup metricGroup, double managedMemoryFraction, boolean isUsingCustomRawKeyedState) throws Exception { //1. 获取task实例信息TaskInfo taskInfo = environment.getTaskInfo(); OperatorSubtaskDescriptionText operatorSubtaskDescription = new OperatorSubtaskDescriptionText( operatorID, operatorClassName, taskInfo.getIndexOfThisSubtask(), taskInfo.getNumberOfParallelSubtasks()); final String operatorIdentifierText = operatorSubtaskDescription.toString(); final PrioritizedOperatorSubtaskState prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates = taskStateManager.prioritizedOperatorState(operatorID); CheckpointableKeyedStateBackend<?> keyedStatedBackend = null; OperatorStateBackend operatorStateBackend = null; CloseableIterable<KeyGroupStatePartitionStreamProvider> rawKeyedStateInputs = null; CloseableIterable<StatePartitionStreamProvider> rawOperatorStateInputs = null; InternalTimeServiceManager<?> timeServiceManager; try { // 创建keyed类型的状态后端// -------------- Keyed State Backend -------------- keyedStatedBackend = keyedStatedBackend( keySerializer, operatorIdentifierText, prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates, streamTaskCloseableRegistry, metricGroup, managedMemoryFraction); //创建operator类型的状态后端// -------------- Operator State Backend -------------- operatorStateBackend = operatorStateBackend( operatorIdentifierText, prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates, streamTaskCloseableRegistry); //创建原生类型状态后端// -------------- Raw State Streams -------------- rawKeyedStateInputs = rawKeyedStateInputs( prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates .getPrioritizedRawKeyedState() .iterator()); streamTaskCloseableRegistry.registerCloseable(rawKeyedStateInputs); rawOperatorStateInputs = rawOperatorStateInputs( prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates .getPrioritizedRawOperatorState() .iterator()); streamTaskCloseableRegistry.registerCloseable(rawOperatorStateInputs); //创建Internal Timer Service Manager// -------------- Internal Timer Service Manager -------------- if (keyedStatedBackend != null) { // if the operator indicates that it is using custom raw keyed state, // then whatever was written in the raw keyed state snapshot was NOT written // by the internal timer services (because there is only ever one user of raw keyed // state); // in this case, timers should not attempt to restore timers from the raw keyed // state. final Iterable<KeyGroupStatePartitionStreamProvider> restoredRawKeyedStateTimers = (prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates.isRestored() && !isUsingCustomRawKeyedState) ? rawKeyedStateInputs : Collections.emptyList(); timeServiceManager = timeServiceManagerProvider.create( keyedStatedBackend, environment.getUserCodeClassLoader().asClassLoader(), keyContext, processingTimeService, restoredRawKeyedStateTimers); } else { timeServiceManager = null; } // -------------- Preparing return value -------------- return new StreamOperatorStateContextImpl( prioritizedOperatorSubtaskStates.getRestoredCheckpointId(), operatorStateBackend, keyedStatedBackend, timeServiceManager, rawOperatorStateInputs, rawKeyedStateInputs); } catch (Exception ex) { 。。。。
}
流程梳理:
- 从environment中获取TaskInfo,并基于Task实例创建OperatorSubtaskDescriptionText。Operator中Task实例的描述信息包含OperatorID、OperatorClassName等,最终用于创建OperatorStateBackend的状态存储后端。
- 创建KeyedStateBackend,KeyedStateBackend是KeyedState的状态管理后端,提供创建和管理KeyedState的方法。
- 创建OperatorStateBackend,OperatorStateBackend是OperatorState的状态管理后端,提供获取和管理OperatorState的接口。
- 创建KeyGroupStatePartitionStreamProvider实例,提供创建和获取原生KeyedState的方法。
- 创建StatePartitionStreamProvider实例,提供创建和获取原生OperatorState的方法。
- 将所有创建出来的托管状态管理后端
keyedStatedBackend和operatorStateBackend、原生状态存储后端rawKeyedStateInputs和rawOperatorStateInputs及timeServiceManager实例,全部封装在StreamOperatorStateContextImpl上下文对象中,并返回给AbstractStreamOperator使用。
小结
StreamTaskStateInitializer.streamOperatorStateContext()方法包含创建托管状态和原生状态管理后端的全过程。StreamOperator的实现类能够从StreamOperatorStateContext中获取这些状态管理组件,并使用它们创建指定类型的状态,最终状态数据会存储在状态管理后端指定的物理介质上,例如堆内存或RocksDB。
StateInitializationContext会被用于算子和UserDefinedFunction中,实现算子或函数中的状态数据操作。
3. StateInitializationContext的接口设计。
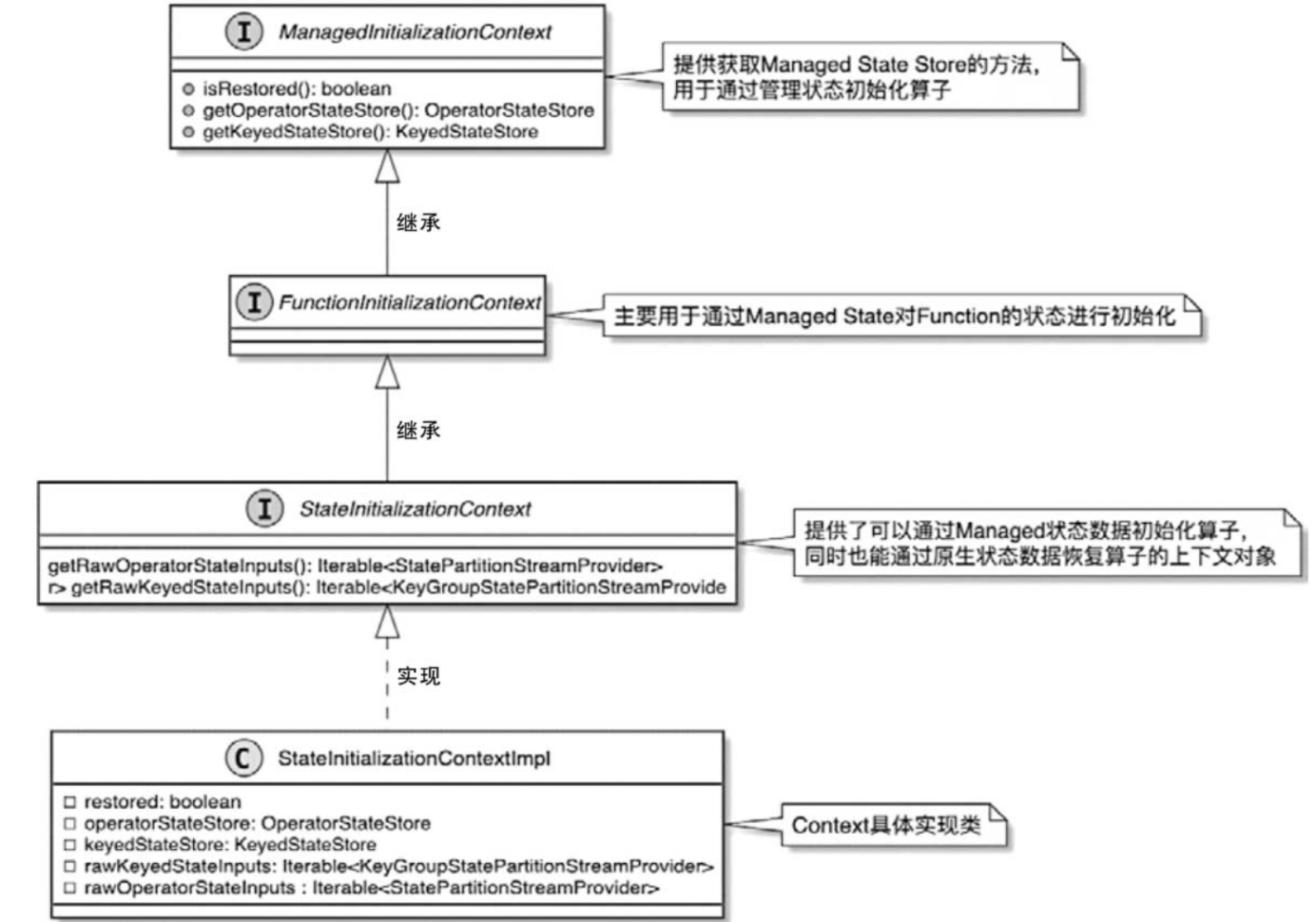
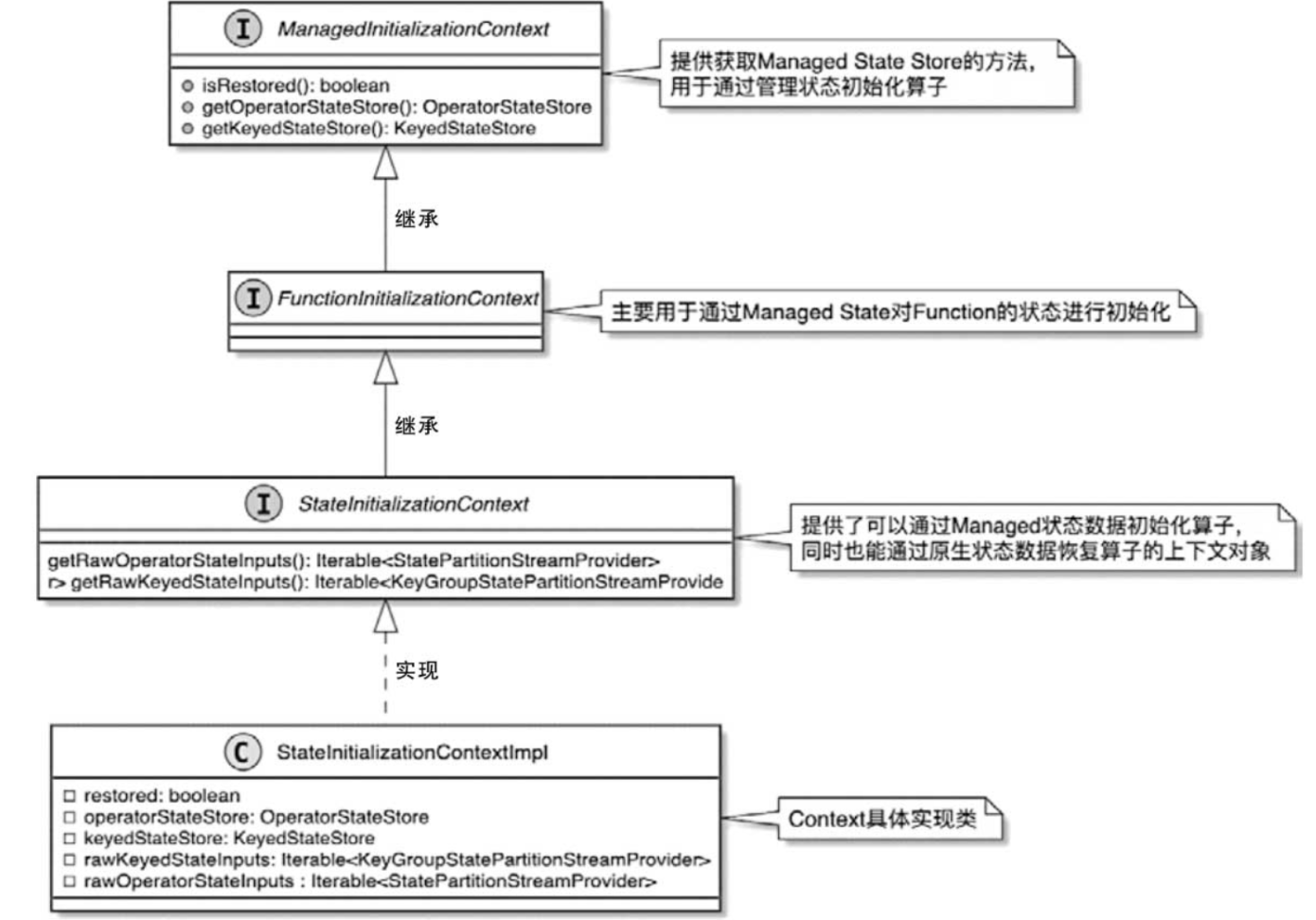
StateInitializationContext接口同时继承了ManagedInitializationContext接口和FunctionInitializationContext接口。StateInitializationContext接口的默认实现类为StateInitializationContextImpl。
ManagedInitializationContext接口提供了托管状态使用的KeyedStateStore和OperatorStateStore获取方法,即KeyedStateBackend和OperatorStateBackend的封装类。算子进行初始化时,会通过KeyedStateStore和OperatorStateStore提供的方法创建和管理指定类型的托管状态。
FunctionInitializationContext提供了用户自定义函数状态数据初始化需要的方法。它和ManagedInitializationContext保持一致,这主要是为了和算子使用的上下文进行区分,但两者的操作基本一致。
StateInitializationContext提供了对托管状态数据的管理,并在内部继承和拓展了获取及管理原生状态数据的方法,如getRawOperatorStateInputs()、getRawKeyedStateInputs()等
StateInitializationContextImpl具备操作管理状态和原生状态的能力。基于它可以获取不同类型的状态管理后端,并基于状态管理操作状态数据。
4. 状态初始化举例:UDF状态初始化
在AbstractStreamOperator中调用initializeState(StateInitializationContext context)抽象方法初始化Operator中的状态。这里以AbstractUdfStreamOperator为例说明具体算子、UDF是如何进行状态初始化的。
AbstractUdfStreamOperator.initializeState()方法实际上调用了StreamingFunctionUtils.restoreFunctionState()方法对User-Defined Function中的状态数据进行初始化和恢复,实际上就是将上文创建的StateInitializationContext上下文信息提供给Function接口使用。
public void initializeState(StateInitializationContext context) throws Exception {super.initializeState(context);StreamingFunctionUtils.restoreFunctionState(context, userFunction);
}
恢复函数内部的状态数据涉及Checkpoint的实现,我们会在之后介绍如何在StreamingFunctionUtils.restoreFunctionState()方法中恢复函数中的状态数据。
《Flink设计与实现:核心原理与源码解析》张利兵