浙江住房和城乡建设部网站域名官网
泛型
泛型的理解和好处
看一个需求
请编写程序,在ArrayList中,添加3个Dog对象
Dog对象含有name和age,并输出name和age(要求使用getXxx)
先用传统的方法来解决->引出泛型
package com15.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title Generic01* @package com15.generic* @time 2023/3/1 16:41*/
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Generic01 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add(new Dog("旺财", 10));arrayList.add(new Dog("小黑", 1));arrayList.add(new Dog("大黄", 8));//假如不小心加入了一只猫arrayList.add(new Cat("招财猫", 16));//23行抛出异常ClassCastException//遍历for (Object o : arrayList) {Dog dog = (Dog) o;//向下转型Object -> DogSystem.out.println(dog.getName() + "-" + dog.getAge());}}
}//1. 请编写程序,在ArrayList中,添加3个Dog对象
//2. Dog对象含有name和age,并输出name和age(要求使用getXxx)
class Dog {private String name;private int age;public Dog(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}class Cat {private String name;private int age;public Cat(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}使用传统方法的问题分析
不能对加入到集合ArrayList中的数据类型进行约束(不安全)
遍历的时候,需要进行类型转换,如果集合中数据量较大,对效率有影响
用泛型来解决上面的问题
ArrayList<Dog> arrayList = new ArrayList<Dog>();
package com15.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title Generic02* @package com15.generic* @time 2023/3/1 16:57*/
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Generic02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//传统方法解决=>使用泛型//解读//1.当ArrayList<Dog>表示存放放到ArrayList集合中的元素是Dog类型//2.如果编译器发现添加的类型,不满足要求,就会报错//3.在遍历的时候,可以直接取出Dog类型而不是Object//4.public class ArrayList<E> {} E称为泛型,那么Dog->EArrayList<Dog> arrayList = new ArrayList<Dog>();arrayList.add(new Dog("旺财", 10));arrayList.add(new Dog("小黑", 1));arrayList.add(new Dog("大黄", 8));//假如不小心加入了一只猫
// arrayList.add(new Cat("招财猫", 16));//抛出异常ClassCastException//遍历System.out.println("====使用泛型====");for (Dog o : arrayList) {System.out.println(o.getName() + "-" + o.getAge());}}
}//1. 请编写程序,在ArrayList中,添加3个Dog对象
//2. Dog对象含有name和age,并输出name和age(要求使用getXxx)
//3.使用泛型解决问题
class Dog {private String name;private int age;public Dog(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}class Cat {private String name;private int age;public Cat(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}泛型的好处
编译时,检查添加元素的类型,提高了安全性
减少了类型转换的次数,提高了效率
不使用泛型
Dog-加入->Object-取出->Dog//放入到ArrayList会先转成Object,再取出时,还需要转换成Dog
使用泛型
Dog->Dog->Dog//放入时,和取出时,不需要类型转换,提高效率
不再提示编译警告
泛型的介绍
int a = 10;
理解:泛(广泛)型(类型)=>Integer, String, Dog
泛型又称参数化模型,是JDK5.0出现的新特性,解决数据类型的安全性问题
在类声明或实例化时只要指定好需要的具体的类型即可
Java泛型可以保证如果程序在编译时没有发出警告,运行时就不会产生ClassCastException异常。同时,代码更加简洁、健壮
泛型的作用是:可以在类声明时通过一个标识表示类中某个属性的类型,或者是某个方法的返回值的类型,或者是参数模型
package com15.generic;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title Generic03* @package com15.generic* @time 2023/3/1 18:30*/
public class Generic03 {public static void main(String[] args) {//注意:特别强调,E表示s的数据类型,该数据类型在定义Person对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定E是什么类型Person<String> person = new Person<>("甲柒");person.show();//String/*解读class Person<E>{String s;//E表示s的数据类型,该数据类型在定义Person对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定E是什么类型public Person(String s) {//E也可以是参数类型this.s = s;}public String f(){//返回类型使用Ereturn s;}}*/Person<Integer> person1 = new Person<Integer>(100);person1.show();//Integer/*class Person{Integer s;//E表示s的数据类型,该数据类型在定义Person对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定E是什么类型public Person(Integer s) {//E也可以是参数类型this.s = s;}public Integer f(){//返回类型使用Ereturn s;}}*/}
}//泛型的作用是:可以在类声明时通过一个标识表示类中某个属性的类型
//,或者是某个方法的返回值的类型,或者是参数模型
class Person<E> {E s;//E表示s的数据类型,该数据类型在定义Person对象的时候指定,即在编译期间,就确定E是什么类型public Person(E s) {//E也可以是参数类型this.s = s;}public E f() {//返回类型使用Ereturn s;}public void show() {System.out.println(s.getClass());}
}泛型的语法
泛型的声明
intterface接口<T>{}和class类<K, V>{}
//比如:List,ArrayList
说明:
其中,T,K,V不代表值,而是表示类型
任意字母都可以,常用T表示,是Type的缩写
泛型的实例化
要在类名后面指定类型参数的值(类型),如:
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<String>();
Iterator<Customer> iterator = customers.iterator();
泛型语法和使用
泛型使用举例
举例说明,泛型在HashSet,HashMap的使用情况
练习:
创建3个学生对象
放入到HashSet中学生对象
放入到HashMap中,要求Key是String name,Value就是学生对象
使用两种方式遍历
package com15.generic;import java.util.*;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title GenericExercise* @package com15.generic* @time 2023/3/1 20:11*/
public class GenericExercise {public static void main(String[] args) {//HashSet<Student> hashSet = new HashSet<Student>();hashSet.add(new Student("tom", 16));hashSet.add(new Student("jerry", 6));hashSet.add(new Student("tom", 18));hashSet.add(new Student("mike", 32));//遍历System.out.println("++++++增强for遍历hashSet中的对象+++++");for (Student student : hashSet) {System.out.println(student);}//使用泛型后,下面的语句就报错
// hashSet.add(300);System.out.println("++++++while遍历hashSet中的对象+++++");Iterator<Student> iterator = hashSet.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Student student = iterator.next();System.out.println(student);}//2.使用泛型方式给HashMap放入3个对象HashMap<String, Student> hashMap = new HashMap<String, Student>();hashMap.put("tom", new Student("tom", 30));hashMap.put("smith", new Student("smith", 22));hashMap.put("甲柒", new Student("甲柒", 30));hashMap.put("價柒", new Student("價柒", 30));//迭代器Entry/*public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;}*/Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Student>> iterator1 = entries.iterator();System.out.println("========遍历iterator1中的对象========");while (iterator1.hasNext()) {Map.Entry<String, Student> entry = iterator1.next();System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-" + entry.getValue());}}
}// 1. 创建3个学生对象
// 2. 放入到HashSet中学生对象
// 3. 放入到HashMap中,要求Key是String name,Value就是学生对象
// 4. 使用两种方式遍历
class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}泛型使用的注意事项和细节
interface List<T>{},public class HashSet<E>{}.....
说明:T,E只能是引用类型,不能是基本数据类型
判断下列语句是否正确
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();//ok
List<int> list2 = new ArrayList<int>();//错误在指定泛型具体类型后,可以传入该类型或者其子类型
泛型使用形式
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();如果这样写
List list3 = new ArrayList();//默认给他的泛型是[<E> E就是Object]
package com15.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title GenericDetail* @package com15.generic* @time 2023/3/1 21:10*/
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class GenericDetail {public static void main(String[] args) {//1.给泛型指向数据类型是 要求 必须是 引用类型,// 不能是 基本数据类型(byte,short,int,long,char,boolean,float,double)List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();//ok
// List<int> list2 = new ArrayList<int>();//错误//2.说明//因为E指定了A类型,构造器传入了new A()//在给泛型指定具体类型后,可以传入该类型或者其子类型Pig<A> aPig = new Pig<A>(new A());aPig.f();Pig<A> aPig2 = new Pig<A>(new B());aPig2.f();//3.泛型的使用形式ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();//在实际开发中,往往简写//编译器会进行类型推断,推荐使用下面写法ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list4 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<Pig> pigs = new ArrayList<>();//4.如果是这样写 泛型默认是 ObjectArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();//等价ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();arrayList.add("XX");/*public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}*/Tiger tiger = new Tiger();}
}class Tiger<E> {E e;public Tiger() {}public Tiger(E e) {this.e = e;}
}class A {
}class B extends A {
}class Pig<E> {//E e;public Pig(E e) {this.e = e;}public void f() {System.out.println(e.getClass());//运行类型}
}泛型练习题
定义Employee类
该类包含:private成员变量name,sal,birthday,其中birthday为MyDate类的对象
为每一个属性定义getter,setter方法
重写toString方法输出name,sal,birthday
MyDate类包含:private成员变量month,day,year;并为每一个属性定义getter,setter方法
创建该类的3个对象,并把这些对象放入ArrayList集合中(ArrayList需要使用泛型来定义),对集合中的元素进行排序,并遍历输出:
排序方式:调用ArrayList的sort方法,传入Comparator对象[使用泛型],先按照name排序,如果name相同,则按生日日期的先后排序。[即:定制排序]
package com15.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title GenericExercise02* @package com15.generic* @time 2023/3/5 18:22*/
//@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class GenericExercise02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Employee employee1 = new Employee("tom", 3000.00, new MyDate(1988, 9, 27));Employee employee2 = new Employee("tom", 2700.00, new MyDate(1969, 9, 6));Employee employee3 = new Employee("甲柒", 6900.00, new MyDate(2000, 12, 30));ArrayList<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<>();employees.add(employee1);employees.add(employee2);employees.add(employee3);System.out.println("employees=" + employees);System.out.println("====对员工进行排序====");employees.sort(new Comparator<Employee>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Employee o1, Employee o2) {//先按照name排序,如果name相同,则按照生日日期的先后排序。[即:定制排序]//先对传入的参数进行验证if (!(o1 instanceof Employee && o2 instanceof Employee)) {System.out.println("类型不正确!!!!");return 0;}//比较nameint i = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());if (i != 0) {return i;}//下面是对birthday的比较,因此,最好把下面这段比较,放在MyDate类中//封装后,将来的可维护性,复用性就大大增强了
// //如果name相同就继续比较,就比较birthday - year
// int yearMinus = o1.getBirthday().getYear() - o2.getBirthday().getYear();
// if (yearMinus != 0) {
// return yearMinus;
// }
// //如果year相同就继续比较,就比较birthday - month
// int monthMinus = o1.getBirthday().getMonth() - o2.getBirthday().getMonth();
// if (monthMinus != 0) {
// return monthMinus;
// }
// //如果month相同就继续比较,就比较birthday - day
//
// return o1.getBirthday().getDay() - o2.getBirthday().getDay();return o1.getBirthday().compareTo(o2.getBirthday());}});System.out.println("=====排序后的结果=====");System.out.println(employees);}
}//定义Employee类
//1. 该类包含:private成员变量name,sal,birthday,
// 其中birthday为MyDate类的对象
//2. 为每一个属性定义getter,setter方法
//3. 重写toString方法输出name,sal,birthday
//4. MyDate类包含:private成员变量month,day,year;
// 并为每一个属性定义getter,setter方法
//5. 创建该类的3个对象,并把这些对象放入ArrayList集合中
// (ArrayList需要使用泛型来定义),对集合中的元素进行排序,并遍历输出:
//排序方式:调用ArrayList的sort方法,传入Comparator对象[使用泛型],
// 先按照name排序,如果name相同,则按生日日期的先后排序。[即:定制排序]
class Employee {private String name;private double sal;private MyDate birthday;public Employee(String name, double sal, MyDate birthday) {this.name = name;this.sal = sal;this.birthday = birthday;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getSal() {return sal;}public void setSal(double sal) {this.sal = sal;}public MyDate getBirthday() {return birthday;}public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "\nEmployee{" +"name=" + name +", sal=" + sal +", birthday=" + birthday +'}';}
}class MyDate implements Comparable<MyDate> {private int year;private int month;private int day;public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;}public int getYear() {return year;}public void setYear(int year) {this.year = year;}public int getMonth() {return month;}public void setMonth(int month) {this.month = month;}public int getDay() {return day;}public void setDay(int day) {this.day = day;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return year + "-" + month + "-" + day;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(MyDate o) {//把year-month-day比较放在这里//如果name相同就继续比较,就比较birthday - yearint yearMinus = year - o.getYear();if (yearMinus != 0) {return yearMinus;}//如果year相同就继续比较,就比较birthday - monthint monthMinus = month - o.getMonth();if (monthMinus != 0) {return monthMinus;}//如果month相同就继续比较,就比较birthday - dayreturn day - o.getDay();}
}自定义泛型
自定义泛型类
基本语法
class 类名<T, R> {//...
//成员
}注意细节
普通成员可以使用泛型(属性、方法)
使用泛型的数组,不能初始化
静态方法中不能使用类的泛型
泛型类的类型,是在创建对象时确定的(因为创建对形象时,需要指定确定类型)
如果在创建对象时,没有指定类型,默认位Object
package com15.customgeneric;import java.util.Arrays;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title CustomGeneric_* @package com15.customgeneric* @time 2023/3/5 23:01*/
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class CustomGeneric_ {public static void main(String[] args) {//T=Double,R=String,M=IntegerTiger<Double, String, Integer> john = new Tiger<>("john");john.setT(10.98);//ok
// john.setT("abc");//错误,类型不对System.out.println(john);Tiger tiger = new Tiger("john~~~");//ok,T默认为Object (T=Object,R=Object,M=Object)tiger.setT("yy");//ok,因为T默认为Object,"yy"为String类型 是 Object子类System.out.println("tiger=" + tiger);}
}//解读
//1.Tiger后面泛型,所以把Tiger就称为自定义泛型类
//2.T,R,M泛型的标识符,一般是单个大写字母
//3.泛型标识符可以有多个
//4.普通成员可以使用泛型(属性、方法)
//5.使用泛型的数组,不能初始化
//6.静态方法中不能使用类的泛型
class Tiger<T, R, M> {String name;T t;//属性使用到泛型R r;M m;//因为数组在new不能确定T的类型,就无法在内存开空间
// T[] ts = new T[8];T[] ts;//因为静态是和类相关的,在类加载时,对象还没有创建//所以,如果静态方法和静态属性使用了泛型,JVM就无法完成初始化
// static R r2;//错误R r3;//okpublic Tiger(String name) {this.name = name;}public Tiger(T t, R r, M m) {//构造器使用泛型this.t = t;this.r = r;this.m = m;}public Tiger(String name, T t, R r, M m) {//构造器使用泛型this.name = name;this.t = t;this.r = r;this.m = m;}public void m1(M m) {//ok}
// public static void m2(M m) {//错误
// }public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public T getT() {return t;}public void setT(T t) {this.t = t;}public R getR() {return r;}public void setR(R r) {//方法使用到泛型this.r = r;}public M getM() {return m;}public void setM(M m) {this.m = m;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Tiger{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", t=" + t +", r=" + r +", m=" + m +", ts=" + Arrays.toString(ts) +", r3=" + r3 +'}';}
}自定义泛型接口
基本语法
interface 接口名 <T, R....>{
}注意细节
接口中,静态成员也不能使用泛型(这个和泛型类规定一样)
泛型接口的类型,在继承接口或者实现接口时确定
没有指定类型,默认为Object
package com15.customgeneric;/*** 泛型接口使用的说明* 1.在接口中,静态成员也不能使用泛型* 2.泛型接口的类型,在继承接口或者实现接口时确定* 3.没有指定类型,默认为Object** @param <U>* @param <R>*/
interface IUsb<U, R> {int n = 10;//U name;//不能这样使用//普通方法中,可以使用接口泛型R get(U u);void hi(R r);void run(R r1, R r2, U u1, U u2);//在JDK8中,可以在接口中,使用默认方法,也可以使用泛型default R method(U u) {return null;}
}//在继承接口 指定泛型接口的类型
interface IA extends IUsb<String, Double> {}//当我们去实现IA接口时,因为IA在继承IUsu接口时,指定了U为String R为Double
//在实现IUsu接口的方法时,使用String替换U,是Double替换R
class AA implements IA {@Overridepublic Double get(String s) {return null;}@Overridepublic void hi(Double aDouble) {}@Overridepublic void run(Double r1, Double r2, String u1, String u2) {}
}//实现接口时,直接指定泛型接口的类型
//给U指定Integer给R指定了Float
//所以,当我们实现IUsb方法时,会使用Integer替换U,使用Float替换R
class BB implements IUsb<Integer, Float> {@Overridepublic Float get(Integer integer) {return null;}@Overridepublic void hi(Float aFloat) {}@Overridepublic void run(Float r1, Float r2, Integer u1, Integer u2) {}
}//没有指定类型,默认为Object
//建议直接写成class CC implements IUsb<Object, Object>
class CC implements IUsb {//等价class CC implements IUsb<Object, Object>@Overridepublic Object get(Object o) {return null;}@Overridepublic void hi(Object o) {}@Overridepublic void run(Object r1, Object r2, Object u1, Object u2) {}
}/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title CustomInterfaceGeneric* @package com15.customgeneric* @time 2023/3/10 9:21*/
public class CustomInterfaceGeneric {public static void main(String[] args) {}
}自定义泛型方法
基本语法
修饰符 <T, R...>返回类型 方法名(参数列表) {
}注意细节
泛型方法,可以定义在普通类中,也可以定义在泛型类中
当泛型方法被调用时,类型会确定
public void eat(E e) {},修饰符后没有<T, R....> eat方法不是泛型方法,而是使用了泛型
应用案例
package com15.customgeneric;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title CustomMethodGeneric* @package com15.customgeneric* @time 2023/3/10 9:54*/
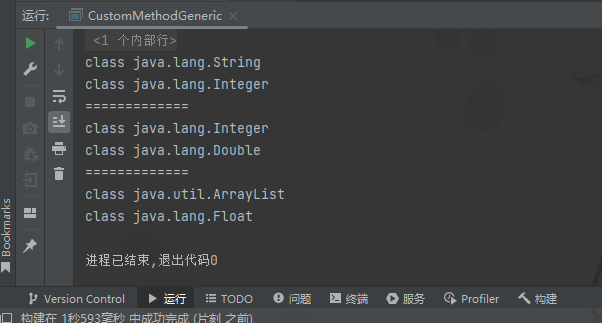
public class CustomMethodGeneric {public static void main(String[] args) {Car car = new Car();car.fly("宝马", 1000);//当调用方法时,传入参数,编译器,就会确定类型System.out.println("=============");car.fly(3000, 1000.23);//当调用方法时,传入参数,编译器,就会确定类型System.out.println("=============");//测试//T->String,R->ArrayListFish<String, ArrayList> fish = new Fish<>();fish.hello(new ArrayList(), 1123.32f);}
}//1. 泛型方法,可以定义在普通类中,也可以定义在泛型类中
//2. 当泛型方法被调用时,类型会确定
//3. public void eat(E e) {},修饰符后没有<T, R....> eat方法不是泛型方法,而是使用了泛型
class Car {//普通类public void run() {//普通方法}//说明//1.<T, R>就是泛型//2.是提供给fly使用的public <T, R> void fly(T t, R r) {//泛型方法System.out.println(t.getClass());//自动装箱StringSystem.out.println(r.getClass());//自动装箱Integer}
}class Fish<T, R> {//泛型类public void run() {//普通方法}public <U, M> void eat(U u, M m) {//泛型方法}//说明//1.下面hi方法不是泛型方法//2.是hi方法使用了类声明的泛型public void hi(T t) {}//泛型方法,可以使用类声明的泛型,也可以使用自己声明泛型public <K> void hello(R r, K k) {System.out.println(r.getClass());System.out.println(k.getClass());}
}
练习题
下面代码是否正确,如果有错误,修改正确,并说明输出什么
package com15.customgeneric;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title CustomMethodGenericExercise* @package com15.customgeneric* @time 2023/3/10 10:31*/
public class CustomMethodGenericExercise {public static void main(String[] args) {Apple<String, Integer, Double> apple = new Apple<>();apple.fly(10);//会被自动装箱 Integer 10 输出Integerapple.fly(new Dog());//Dog}
}class Apple<T, R, M> {//自定义泛型类public <E> void fly(E e) {//泛型方法System.out.println(e.getClass().getSimpleName());}// public void eat(U u) {//错误,因为U没有声明
// }public void run(M m) {}//ok
}class Dog {
}泛型的继承和通配符
泛型的继承和通配符说明
泛型不具备继承性
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<String>();//错误<?>:支持任意泛型类型
<? extrnds A>:支持A类以及A类的子类,规定了泛型的上线
<? super A>:支持A类以及A类的父类,不限于直接父类,规定了泛型的下线
案例
package com15.customgeneric;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title GenericExtends* @package com15.customgeneric* @time 2023/3/11 8:54*/
public class GenericExtends {public static void main(String[] args) {Object o = new String("xx");//泛型没有继承性
// List<Object> list = new ArrayList<String>();//错误//举例说明下面三个方法的使用ArrayList<Object> list1 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<A> list3 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<B> list4 = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<C> list5 = new ArrayList<>();//如果是 List<?> c 可以接受任意的泛型类型printCollection1(list1);printCollection1(list2);printCollection1(list3);printCollection1(list4);printCollection1(list5);//List<? extends A> c 表示 上限,可以接受A 或者A的子类
// printCollection2(list1);//错误
// printCollection2(list2);//错误printCollection2(list3);//okprintCollection2(list4);//okprintCollection2(list5);//ok//List<? super A> c 子类类名A:支持A类以及A类的父类,不限于直接父类,printCollection3(list1);//ok
// printCollection3(list2);//错误printCollection3(list3);//ok
// printCollection3(list4);//错误
// printCollection3(list5);//错误}//方法//说明:List<?>表示 任意的泛型类型都可以接受public static void printCollection1(List<?> c) {for (Object object : c) {//通配符,取出时,就是ObjectSystem.out.println(object);}}//? extends A 表示 上限,可以接受A 或者A的子类public static void printCollection2(List<? extends A> c) {for (Object object : c) {System.out.println(object);}}//? super A 子类类名A:支持A类以及A类的父类,不限于直接父类,//规定了泛型的下线public static void printCollection3(List<? super A> c) {for (Object object : c) {System.out.println(object);}}}class A {}class B extends A {}class C extends B {}JUnit
为什么需要JUnit
一个类有很多功能代码需要测试,为了测试,就需要写入到main方法中
如果有多个功能代码测试,就需要来回注销,切换很麻烦
如果可以直接运行一个方法,就方便很多,并且可以给出相关信息就好了->JUnit
package com15.junit_;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;/*** @author 甲柒* @version 1.0* @title JUnit_* @package com15.junit_* @time 2023/3/11 9:51*/
public class JUnit_ {public static void main(String[] args) {//传统方式//new JUnit_().m1();//new JUnit_().m2();}@Testpublic void m1() {System.out.println("m1方法被调用");}@Testpublic void m2() {System.out.println("m2方法被调用");}
}