高新区网站建设的建议点击排名优化
装饰模式
- 装饰模型
- 装饰模式示例
- 商场收银程序(简单工厂+策略+装饰模式实现)
- 装饰模式总结
装饰模型
装饰模式(Decorator),动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更为灵活。
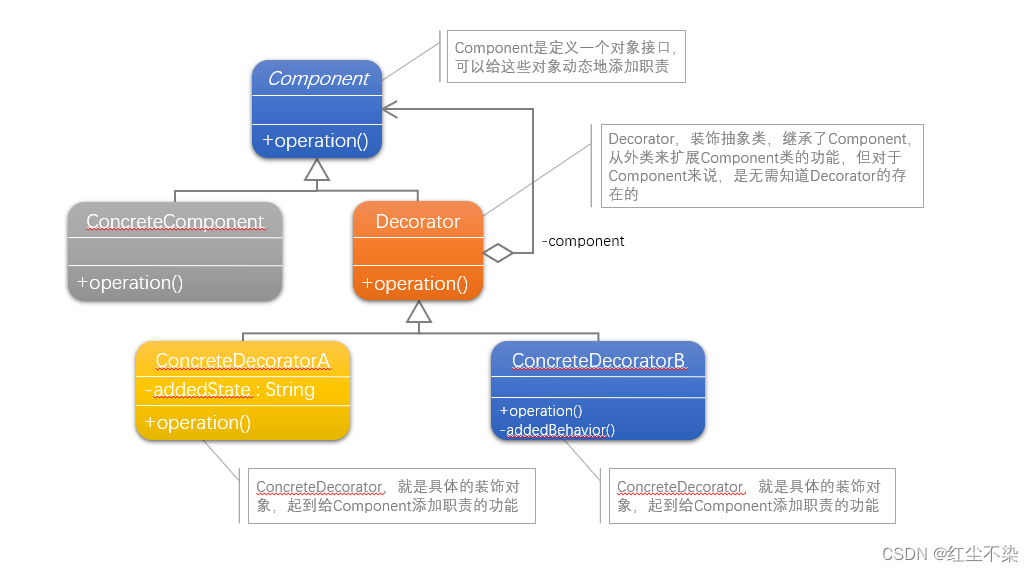
Component 是定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加职责。
ConcreateComponent 是定义了一个具体的对象,也可以给这个对象添加一些职责。
Decorator,装饰抽象类,继承了 Component,从外类来扩展 Component 类的功能,但对应Component 来说,是无须知道 Decorator的存在。
ConcreateDecorator 就是具体的装饰对象,起到给 Component 添加职责的功能。
// Component类
abstract class Component {public abstract void Operation();
}
// ConcreteComponent类
class ConcreteComponent extends Component {public void Operation() {System.out.println("具体对象的实际操作");}
}
//Decorator类
abstract class Decorator extends Component {protected Component component;//装饰一个Component对象public void SetComponent(Component component) {this.component = component;}//重写Operation(),实际调用component的Operation方法public void Operation() {if (component != null) {component.Operation();}}
}
//ConcreteDecoratorA类
class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator {//本类独有子段,以区别于ConcreteDecoratorB类private String addedState;public void Operation() {//首先运行了原有Component的Operation()super.Operation();this.addedState = "具体装饰对象A的独有操作";//再执行本类独有功能System.out.println(this.addedState);}
}
//ConcreteDecoratorB类
class ConcreteDecoratorB extends Decorator {public void Operation() {//首先运行了原有Component的Operation()super.Operation();//再执行本类独有功能this.AddedBehavior();}//本类独有方法,以区别于ConcreteDecoratorA类private void AddedBehavior() { System.out.println("具体装饰对象B的独有操作");}
}客户端代码
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){System.out.println("**********************************************"); System.out.println("《大话设计模式》代码样例");System.out.println(); ConcreteComponent c = new ConcreteComponent();ConcreteDecoratorA d1 = new ConcreteDecoratorA();ConcreteDecoratorB d2 = new ConcreteDecoratorB();//首先用d1来包装c,扩展对象c的方法d1.SetComponent(c); //再用有来包装d1,扩展对象d1的方法d2.SetComponent(d1);//最终执行d2的Operation()d2.Operation(); System.out.println();System.out.println("**********************************************");}
}
装饰模式利用SetComponent来对对象进行包装,这样每个装饰对象的实现和如何使用这个对象分离开了,每个装饰对象只关心自己的功能,不需要关心如何被添加到对象链中。
如果只有一个ConcreteComponent 类而没有抽象的 Component 类,那么 Decorator 类可以是 ConcreteComponent 的一个子类。
同样道理,如果只要一个 ConcreteDecorator 类,那么就没有必要建立一个单独的 Decorator 类,而可以把 Decorator 和 ConcreteDecorator 的责任合并成一个类。
装饰模式示例
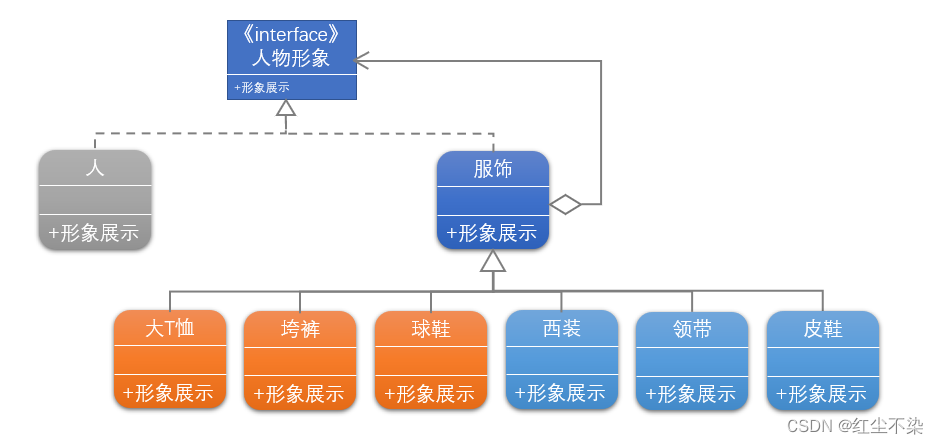
人物形象接口
public interface ICharacter {public void show();
}
具体人类
public class Person implements ICharacter {private String name;public Person(String name) {this.name = name;}public void show() {System.out.println("装扮的"+name);}
}
服饰类
public class Finery implements ICharacter {protected ICharacter component;public void decorate(ICharacter component) {this.component=component;}public void show() {if (this.component != null){this.component.show();}}
}
具体服饰类(ConcreteDecorator)
public class LeatherShoes extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 皮鞋");super.show();}
}
public class BigTrouser extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 垮裤");super.show();}
}
public class TShirts extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 大T恤");super.show();}
}
public class Tie extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 领带");super.show();}
}
public class Suit extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 西装");super.show();}
}
public class Strawhat extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 草帽");super.show();}
}
public class Sneakers extends Finery {public void show(){System.out.print(" 球鞋");super.show();}
}
客户端代码
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){System.out.println("**********************************************"); System.out.println("《大话设计模式》代码样例");System.out.println(); Person xc = new Person("小菜");System.out.println(" 第一种装扮:");Sneakers pqx = new Sneakers(); //生成球鞋实例pqx.decorate(xc); //球鞋装饰小菜BigTrouser kk = new BigTrouser(); //生成垮裤实例kk.decorate(pqx); //垮裤装饰“有球鞋装饰的小菜”TShirts dtx = new TShirts(); //生成T恤实例dtx.decorate(kk); //T恤装饰“有垮裤球鞋装饰的小菜”dtx.show(); //执行形象展示System.out.println(" 第二种装扮:");LeatherShoes px = new LeatherShoes();//生成皮鞋实例px.decorate(xc); //皮鞋装饰小菜Tie ld = new Tie(); //生成领带实例ld.decorate(px); //领带装饰“有皮鞋装饰的小菜”Suit xz = new Suit(); //生成西装实例xz.decorate(ld); //西装装饰“有领带皮鞋装饰的小菜”xz.show(); //执行形象展示System.out.println(" 第三种装扮:");Sneakers pqx2 = new Sneakers(); //生成球鞋实例pqx2.decorate(xc); //球鞋装饰小菜LeatherShoes px2 = new LeatherShoes();//生成皮鞋实例px2.decorate(pqx2); //皮鞋装饰“有球鞋装饰的小菜”BigTrouser kk2 = new BigTrouser(); //生成垮裤实例kk2.decorate(px2); //垮裤装饰“有皮鞋球鞋装饰的小菜”Tie ld2 = new Tie(); //生成领带实例ld2.decorate(kk2); //领带装饰“有垮裤皮鞋球鞋装饰的小菜”Strawhat cm2 = new Strawhat(); //生成草帽实例cm2.decorate(ld2); //草帽装饰“有领带垮裤皮鞋球鞋装饰的小菜”cm2.show(); //执行形象展示System.out.println();System.out.println("**********************************************");}
}
商场收银程序(简单工厂+策略+装饰模式实现)
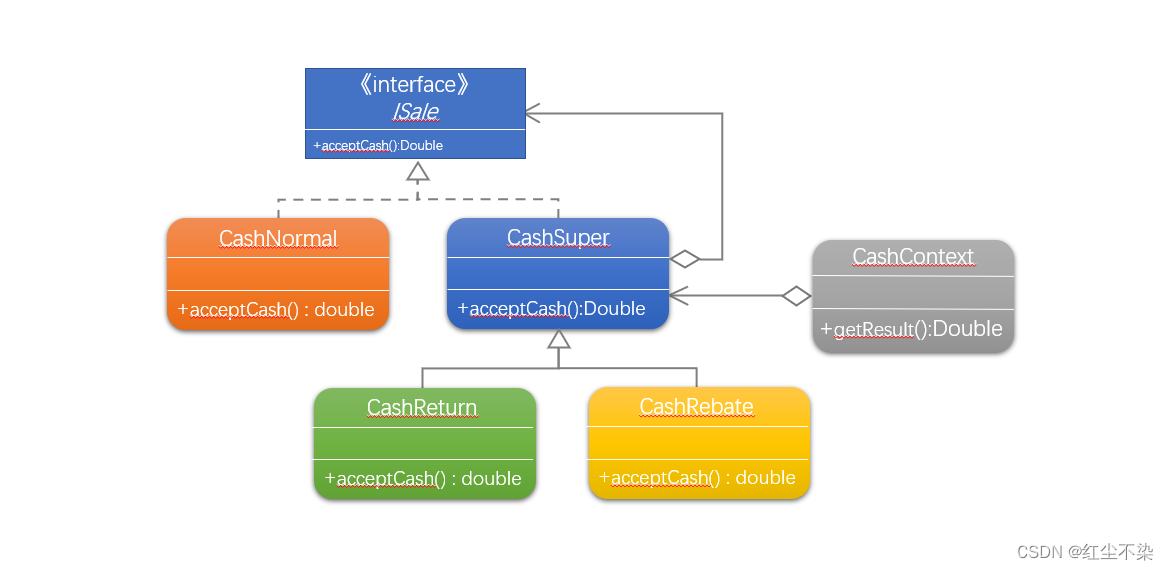
ISale接口:用作装饰模式里的 Component。
CashNormal: 用作装饰模式里的 ConcreteComponent。
CashSuper: 用作装饰模式里的 Decorator 。
CashReturn:用作装饰模式里的 ConcreateDecorator 。
public interface ISale {public double acceptCash(double price,int num);
}
// 正常收费,原价返回
public class CashNormal implements ISale {public double acceptCash(double price,int num){return price * num;}
}
public class CashSuper implements ISale {protected ISale component;//装饰对象public void decorate(ISale component) {this.component=component;}public double acceptCash(double price,int num){var result = 0d;if (this.component != null){//若装饰对象存在,则执行装饰的算法运算result = this.component.acceptCash(price,num); }return result;}
}
public class CashRebate extends CashSuper {private double moneyRebate = 1d;//打折收费。初始化时必需输入折扣率。八折就输入0.8public CashRebate(double moneyRebate){this.moneyRebate = moneyRebate;}//计算收费时需要在原价基础上乘以折扣率public double acceptCash(double price,int num){double result = price * num * this.moneyRebate;return super.acceptCash(result,1);}
}public class CashReturn extends CashSuper {private double moneyCondition = 0d; //返利条件private double moneyReturn = 0d; //返利值//返利收费。初始化时需要输入返利条件和返利值。//比如“满300返100”,就是moneyCondition=300,moneyReturn=100public CashReturn(double moneyCondition,double moneyReturn){this.moneyCondition = moneyCondition;this.moneyReturn = moneyReturn;}//计算收费时,当达到返利条件,就原价减去返利值public double acceptCash(double price,int num){double result = price * num;if (moneyCondition>0 && result >= moneyCondition)result = result - Math.floor(result / moneyCondition) * moneyReturn; return super.acceptCash(result,1); }
}
public class CashContext {private ISale cs; //声明一个ISale接口对象 //通过构造方法,传入具体的收费策略public CashContext(int cashType){switch(cashType){case 1:this.cs = new CashNormal();break;case 2:this.cs = new CashRebate(0.8d);break;case 3:this.cs = new CashRebate(0.7d);break;case 4:this.cs = new CashReturn(300d,100d);break;case 5://先打8折,再满300返100// 装饰模式CashNormal cn = new CashNormal();CashReturn cr1 = new CashReturn(300d,100d); CashRebate cr2 = new CashRebate(0.8d);cr1.decorate(cn); //用满300返100算法包装基本的原价算法cr2.decorate(cr1); //打8折算法装饰满300返100算法this.cs = cr2; //将包装好的算法组合引用传递给cs对象break;case 6://先满200返50,再打7折// 装饰模式CashNormal cn2 = new CashNormal();CashRebate cr3 = new CashRebate(0.7d);CashReturn cr4 = new CashReturn(200d,50d); cr3.decorate(cn2); //用打7折算法包装基本的原价算法cr4.decorate(cr3); //满200返50算法装饰打7折算法this.cs = cr4; //将包装好的算法组合引用传递给cs对象break;}}public double getResult(double price,int num){// 根据收费策略的不同,获得计算结果return this.cs.acceptCash(price,num);}
}
客户端代码
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args){System.out.println("**********************************************"); System.out.println("《大话设计模式》代码样例");System.out.println(); int discount = 0; //商品折扣模式double price = 0d; //商品单价int num = 0; //商品购买数量double totalPrices = 0d;//当前商品合计费用double total = 0d; //总计所有商品费用Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);do {System.out.println("商品折扣模式如下:"); System.out.println("1.正常收费"); System.out.println("2.打八折"); System.out.println("3.打七折"); System.out.println("4.满300送100"); System.out.println("5.先打8折,再满300送100"); System.out.println("6.先满200送50,再打7折"); System.out.println("请输入商品折扣模式:"); discount = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());System.out.println("请输入商品单价:"); price = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());System.out.println("请输入商品数量:"); num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());System.out.println(); if (price>0 && num>0){//根据用户输入,将对应的策略对象作为参数传入CashContext对象中CashContext cc = new CashContext(discount);//通过Context的getResult方法的调用,可以得到收取费用的结果//让具体算法与客户进行了隔离totalPrices = cc.getResult(price,num);total = total + totalPrices;System.out.println(); System.out.println("单价:"+ price + "元 数量:"+ num +" 合计:"+ totalPrices +"元"); System.out.println();System.out.println("总计:"+ total+"元"); System.out.println();}}while(price>0 && num>0);System.out.println();System.out.println("**********************************************");}
}
装饰模式总结
装饰模式是为已有功能动态地添加更多功能的一种方式。
当系统需要新功能的时候,是向旧的类中添加新的代码。这些新加的代码通常装饰了原有类的核心职责或主要行为,但这种做法的问题在于,它们在主类中加入了新的字段,新的方法和新的逻辑,从而增加了主类的复杂度。
装饰模式却提供了一个非常好的解决方案,它把每个要装饰的功能放在单独的类中,并让这个类包装它所要装饰的对象,因此,当需要执行特殊行为时,客户代码就可以在运行时根据需要有选择地、按顺序地使用装饰功能包装对象了。
把类中的装饰功能从类中搬移去除,这样可以简化原有的类。这样做的好处就是有效地把类的核心职责和装饰功能区分开了。
